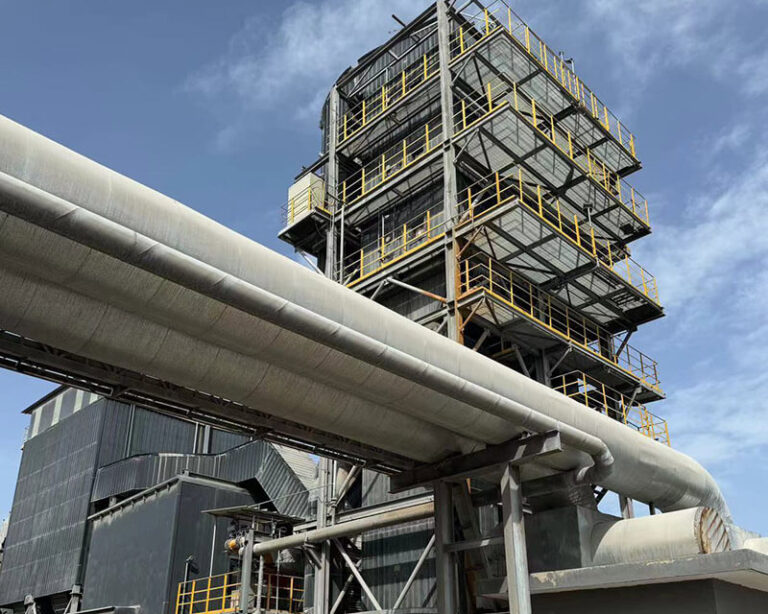
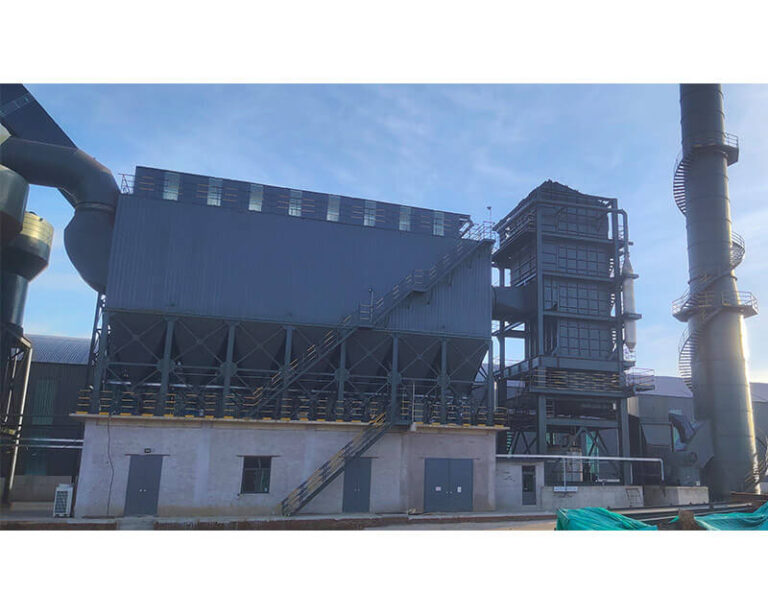
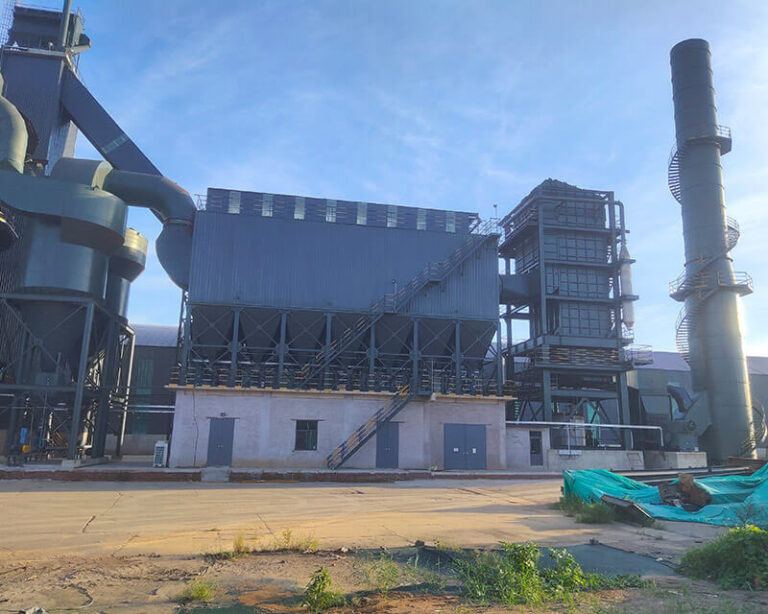
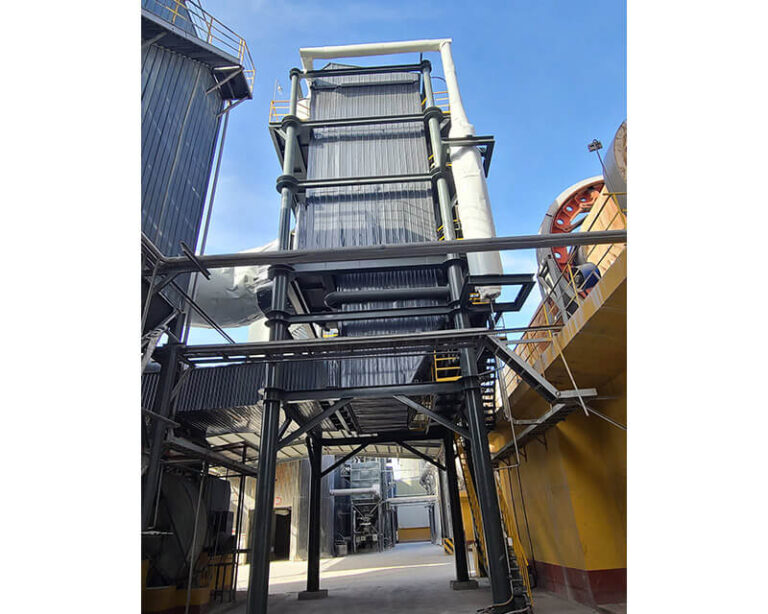
Product Introduction:
Low-temperature SCR denitrification technology refers to the process of using a catalyst to reduce NOx into harmless nitrogen and water vapor at a lower temperature (usually 180°C). Compared with traditional high-temperature SCR technology, low-temperature SCR denitrification technology has higher denitrification efficiency and lower energy consumption, so it has great significance in terms of energy utilization and environmental protection.
Application:
Low-temperature SCR denitrification technology can be applied to various combustion equipment, such as coal-fired boilers, cement kilns, industrial furnaces, steel pellet sintering equipment, etc., and has wide application prospects.
Product Advantages:
01
Reduce NOx emissions, air pollution, and improve air quality;
02
It can promote the transformation of energy utilization methods and promote the optimization and upgrading of energy structure. Reduce environmental pollution and damage by reducing the consumption of traditional energy sources such as coal, fuel oil, and gas.
SCR Denitrification Working Process:
The full name of SCR is Selective Catalytic Reduction. The catalytic reduction method uses a reducing agent such as ammonia or urea to reduce NOx (NO, NO2) in the exhaust gas through the action of a catalyst at a certain temperature, and converts NOx into non-polluting elemental molecular nitrogen (N2). The reaction between NOx and ammonia gas reaction is as follows:
4NO + 4NH3 + O2 → 4N2 + 6H2O
6NO2+8NH3→7N2+12H2O